Title: 80 Disabled Veteran Benefits: Honoring Those Who Served
Introduction:
Disabled veterans have made immense sacrifices for our country, and it is our duty to ensure they receive the support and benefits they deserve. The United States government provides a wide range of benefits to honor these brave men and women who have served in the military. In this article, we will explore 80 disabled veteran benefits available, highlighting the importance of recognizing their contributions and providing them with comprehensive assistance.
Disability Compensation:
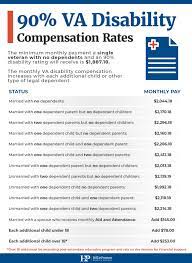
One of the primary benefits available to disabled veterans is disability compensation. This monetary support is provided to veterans who have service-connected disabilities resulting from their time in the military. The amount varies based on the severity of the disability.
Health Care:
Disabled veterans are eligible for comprehensive health care services through the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA). This includes medical treatments, surgeries, mental health care, rehabilitation programs, and access to specialized clinics.
Vocational Rehabilitation and Employment (VR&E):
The VR&E program assists disabled veterans in finding meaningful employment opportunities by providing vocational training, career counseling, job placement assistance, and financial aid for education or retraining.
Home Loans:
The VA offers home loan programs that provide favorable terms and conditions for disabled veterans looking to purchase or modify a home. These loans often require no down payment or private mortgage insurance.
Adapted Housing Grants:
Disabled veterans can apply for grants to adapt their homes according to their specific needs. These grants assist in making homes more accessible by installing ramps, widening doorways, or modifying bathrooms.
Automobile Allowance and Adaptive Equipment:
For those with service-connected disabilities that limit their mobility, an automobile allowance can be granted by the VA to help cover the cost of purchasing a vehicle suitable for their needs. Additionally, adaptive equipment grants are available for modifying vehicles.
Special Monthly Compensation (SMC):
SMC provides additional financial assistance for disabled veterans who have severe disabilities or require aid and attendance. It acknowledges the extra care and support needed due to their service-connected disabilities.
Education and Training:
The Post-9/11 GI Bill and other educational programs offer disabled veterans the opportunity to pursue higher education, vocational training, apprenticeships, or on-the-job training. These benefits cover tuition fees, housing allowances, and book stipends.
Dependents’ Educational Assistance (DEA):
Disabled veterans’ dependents may be eligible for educational assistance through DEA, which provides funding for degree programs, vocational training, apprenticeships, or other educational pursuits.
Survivor Benefits:
In the unfortunate event of a disabled veteran’s death, their surviving spouse or dependents may be entitled to various benefits such as Dependency and Indemnity Compensation (DIC), survivor pension programs, education assistance, and home loan guarantees.
Conclusion:
The 80 disabled veteran benefits available in the United States demonstrate our nation’s commitment to honoring those who have served in the military. These benefits encompass financial assistance, healthcare services, vocational rehabilitation, housing support, education opportunities, and more. It is crucial that we continue to recognize the sacrifices made by disabled veterans and ensure they receive the comprehensive support they need to lead fulfilling lives after their service to our country.
Frequently Asked Questions: Disabled Veteran Benefits Explained
- How do I apply for disabled veteran benefits?
- What types of benefits are available to disabled veterans?
- How do I find out if I am eligible for disability benefits?
- What documents do I need to provide in order to receive disability benefits?
- Is there a time limit on how long I can receive disability benefits?
- Are there any special programs or services available to disabled veterans?
- How does my income affect my eligibility for disability benefits?
- Are there any tax breaks or other financial incentives available to disabled veterans receiving disability benefits?
How do I apply for disabled veteran benefits?
Applying for disabled veteran benefits can be a complex process, but the following steps will guide you through the application process:
- Gather necessary documentation: Collect all relevant documents, including your military service records, medical records, and any other supporting documents related to your disability.
- Determine eligibility: Visit the official website of the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) to review the eligibility criteria for disability benefits. Ensure that your disability is service-connected or aggravated by military service.
- Complete the application form: To apply for disability benefits, you need to fill out VA Form 21-526EZ, which is available online on the VA website. This form requires detailed information about your military service and medical condition.
- Submit supporting documents: Along with your completed application form, include copies of all relevant supporting documents, such as medical records, doctor’s statements, and any additional evidence that supports your claim.
- Submit your application: Once you have completed the necessary forms and gathered all required documents, submit them to the nearest VA regional office. You can do this by mail or online through the VA’s eBenefits portal.
- Attend a Compensation & Pension (C&P) exam: In most cases, after submitting your application, you will be scheduled for a C&P exam. This examination helps assess the severity and extent of your disability.
- Await a decision: The VA will review your application along with all supporting documentation and make a decision regarding your eligibility for disability benefits. This process may take several months due to varying caseloads and complexities.
- Appeal if necessary: If your initial claim is denied or if you believe you deserve a higher rating than assigned, you have the right to appeal within one year from receiving a decision letter from the VA.
- Keep track of communication: Throughout the process, it is essential to maintain copies of all correspondence with the VA and keep track of important dates and deadlines.
- Seek assistance if needed: If you find the application process overwhelming or need help with your claim, consider reaching out to a veterans service organization (VSO) or an accredited VA claims agent or attorney who can provide guidance and support.
Remember, the process may vary depending on individual circumstances, so it’s important to consult official VA resources and seek assistance when needed.
What types of benefits are available to disabled veterans?
Disabled veterans in the United States are eligible for a wide range of benefits, including:
- Disability Compensation: Monetary support provided to veterans with service-connected disabilities.
- Health Care: Comprehensive medical treatments, mental health care, rehabilitation programs, and specialized clinics.
- Vocational Rehabilitation and Employment (VR&E): Assistance with vocational training, career counseling, job placement, and financial aid for education or retraining.
- Home Loans: Favorable terms and conditions for purchasing or modifying homes.
- Adapted Housing Grants: Grants to adapt homes for accessibility needs.
- Automobile Allowance and Adaptive Equipment: Financial assistance for purchasing vehicles or modifying them for disabled veterans’ mobility needs.
- Special Monthly Compensation (SMC): Additional financial assistance for severe disabilities or aid and attendance requirements.
- Education and Training: Post-9/11 GI Bill benefits covering tuition fees, housing allowances, and book stipends for higher education or vocational training.
- Dependents’ Educational Assistance (DEA): Educational assistance programs for disabled veterans’ dependents pursuing degree programs or vocational training.
- Survivor Benefits: DIC, survivor pension programs, education assistance, and home loan guarantees for surviving spouses or dependents of deceased disabled veterans.
These are just some examples of the benefits available to disabled veterans in the United States. The specific eligibility criteria and application processes may vary depending on individual circumstances and the nature of disabilities. It is recommended to contact the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) or visit their website to explore all available benefits in detail.
How do I find out if I am eligible for disability benefits?
To determine if you are eligible for disability benefits, specifically through the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA), you can follow these steps:
- Gather your military and medical records: Collect all relevant documentation, including your discharge papers (DD-214), service treatment records, and any medical evidence related to your disabilities.
- Visit the VA website: Go to the official VA website at www.va.gov and navigate to the “Disability Compensation” section. Here, you will find detailed information about eligibility criteria and the application process.
- Review eligibility requirements: Familiarize yourself with the eligibility requirements for disability benefits. Generally, to be eligible, you must have a current diagnosis of a disability that is connected to your military service or aggravated by it.
- Utilize VA’s eBenefits portal: Consider creating an account on the VA’s eBenefits portal (www.ebenefits.va.gov). This platform allows you to access various resources and tools related to disability benefits, including checking your eligibility status.
- Contact a Veterans Service Officer (VSO): Reach out to a VSO from reputable organizations like Disabled American Veterans (DAV), Veterans of Foreign Wars (VFW), or American Legion. These professionals can provide guidance throughout the application process and help determine your eligibility.
- Schedule a Compensation & Pension (C&P) examination: In most cases, the VA requires applicants to undergo a C&P examination conducted by a VA healthcare professional. This examination helps evaluate the extent of your disabilities and their connection to military service.
- Submit your application: Complete and submit an application for disability compensation through the VA’s online portal or by mailing it to your nearest regional VA office. Ensure that you include all necessary supporting documents, such as medical records and completed forms.
- Follow up on your claim: After submitting your application, regularly check the status of your claim through eBenefits or by contacting the VA’s toll-free number. Be prepared for potential requests for additional information or examinations during the review process.
Remember, the eligibility determination process can vary based on individual circumstances. It is advisable to seek assistance from a VSO or consult with a legal professional specializing in veterans’ benefits to receive personalized guidance throughout the application process.
What documents do I need to provide in order to receive disability benefits?
To apply for disability benefits in the United States, you will need to provide certain documents and information to support your claim. While the specific requirements may vary depending on your circumstances, here are some common documents typically needed:
- Personal Identification: Provide a valid government-issued photo ID (e.g., driver’s license, passport) to verify your identity.
- Social Security Number: You will need to provide your Social Security number as it is used to identify and process your disability claim.
- Medical Records: Gather medical records that document your disability or condition. This includes doctor’s reports, hospital records, test results, and any other relevant medical documentation that supports your claim.
- Work History: Provide a detailed work history including job titles, dates of employment, job duties, and any vocational training or education you have received.
- W-2 Forms or Self-Employment Records: If you have worked as an employee, gather your W-2 forms from previous employers. If you were self-employed, provide tax returns or other financial records that demonstrate your income.
- Military Service Records (if applicable): If you are a veteran applying for disability benefits through the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA), you may need to submit military service records such as DD Form 214 or equivalent documents.
- Financial Information: Prepare information about your current financial situation, including bank statements, mortgage/rental agreements, and any other sources of income or assets you may have.
- Contact Information: Make sure to provide accurate contact information such as address, phone number, and email address so that the relevant authorities can reach out to you regarding your claim.
It is important to note that these are general guidelines, and additional documentation may be required based on individual circumstances or specific disability programs. It is recommended to consult with the appropriate agency responsible for processing disability claims (such as the Social Security Administration or Department of Veterans Affairs) or seek assistance from a qualified professional to ensure you have all the necessary documents for your specific claim.
Is there a time limit on how long I can receive disability benefits?
No, there is no time limit on how long you can receive disability benefits as a disabled veteran. Once you have been granted disability compensation by the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA), you are eligible to receive the benefits for as long as your service-connected disability persists. The VA conducts periodic reviews to assess the severity of your disability and determine if any changes in benefits are necessary. However, if your condition improves significantly and is no longer considered disabling, the VA may reevaluate your eligibility for benefits. It’s important to stay in touch with the VA and provide any necessary updates regarding your health status to ensure continued support.
Are there any special programs or services available to disabled veterans?
Yes, there are several special programs and services available to disabled veterans in addition to the benefits mentioned earlier. Here are a few notable examples:
- VA Caregiver Support Program: This program provides support and resources to caregivers of disabled veterans. It offers training, counseling, respite care, and financial assistance to those who provide care for veterans with service-connected disabilities.
- Prosthetics and Sensory Aids Service: Disabled veterans can access specialized prosthetic devices, such as artificial limbs or hearing aids, through this service. The program aims to enhance the quality of life for veterans with limb loss or sensory impairments.
- Veterans’ Employment and Training Service (VETS): VETS focuses on helping disabled veterans find meaningful employment opportunities by providing job placement assistance, career counseling, resume building, and networking opportunities.
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Programs: The VA offers comprehensive TBI programs that provide specialized care, rehabilitation services, and support for veterans who have experienced traumatic brain injuries during their military service.
- Mental Health Services: The VA places significant emphasis on mental health support for disabled veterans. They offer a range of mental health services including counseling, therapy, substance abuse treatment programs, and suicide prevention resources.
- Adaptive Sports Programs: Disabled veterans can participate in adaptive sports programs organized by the VA or other organizations. These programs promote physical fitness, rehabilitation, camaraderie, and competition among disabled individuals.
- Legal Assistance: Disabled veterans can access legal aid through various programs that offer free or low-cost legal services for issues related to disability benefits claims, estate planning, family law matters, or other legal concerns.
These are just a few examples of the many special programs and services available to disabled veterans. The goal is to provide comprehensive support tailored to their specific needs and challenges arising from their disabilities incurred during military service.
How does my income affect my eligibility for disability benefits?
Your income can have an impact on your eligibility for disability benefits, specifically in relation to certain programs like Supplemental Security Income (SSI) and some aspects of Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI). Here’s a general overview:
Supplemental Security Income (SSI):
SSI is a needs-based program that provides financial assistance to individuals with disabilities who have limited income and resources. To qualify for SSI, both your income and assets must fall within certain limits set by the Social Security Administration (SSA). The exact limits can vary by state.
For SSI, the SSA considers both earned income (wages from work) and unearned income (such as pensions, Social Security benefits, or support from others). They also take into account any resources you own, such as cash, property, or investments. If your income or resources exceed the established limits, it may affect your eligibility for SSI.
Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI):
SSDI is different from SSI in that it is based on your work history rather than financial need. To qualify for SSDI benefits, you must have earned enough work credits through paying Social Security taxes. These credits are based on your earnings and the number of years you’ve worked.
While SSDI does not have strict income limits like SSI, there are certain rules regarding substantial gainful activity (SGA). If you earn above a certain threshold each month ($1,310 in 2021 for non-blind individuals), the SSA may consider you engaged in SGA and therefore not eligible for SSDI benefits.
It’s important to note that even if you exceed the income limits for SSI or earn above the SGA threshold for SSDI, there are still potential work incentives and deductions available that can help offset these limitations. These include programs like Ticket to Work or impairment-related work expenses.
It’s advisable to consult with a disability attorney or contact the SSA directly to get personalized information regarding your specific circumstances and how your income may affect eligibility for disability benefits.
Are there any tax breaks or other financial incentives available to disabled veterans receiving disability benefits?
Yes, disabled veterans receiving disability benefits may be eligible for tax breaks and other financial incentives. Here are a few examples:
- Disability Compensation: Disability compensation received from the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) is generally tax-free. This means that disabled veterans do not need to include this compensation as taxable income on their federal tax returns.
- Property Tax Exemptions: Many states offer property tax exemptions or reductions for disabled veterans. These exemptions vary by state but can provide significant savings on property taxes for eligible veterans.
- Federal Income Tax Credits: Disabled veterans may qualify for certain federal income tax credits, such as the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) or the Child and Dependent Care Credit (CDCC), depending on their income level and family situation.
- VA Home Loan Funding Fee Exemption: Disabled veterans who are eligible for VA home loans may be exempt from paying the VA funding fee, which can result in substantial savings when purchasing a home.
- State-Specific Financial Incentives: Some states offer additional financial incentives to disabled veterans, such as income tax exemptions, sales tax exemptions, vehicle registration fee waivers, or reduced hunting and fishing license fees.
It’s important to note that specific eligibility criteria and benefits vary depending on individual circumstances and the state in which the veteran resides. It is recommended that disabled veterans consult with a qualified tax professional or reach out to local government agencies to understand the specific financial incentives available to them based on their disability status and location.
Remember, these benefits are subject to change based on updates in legislation or government policies, so it’s essential to stay informed about any changes that may affect your eligibility or entitlements.